Mid-Career Professionals: Understanding Career Stages and Terminology
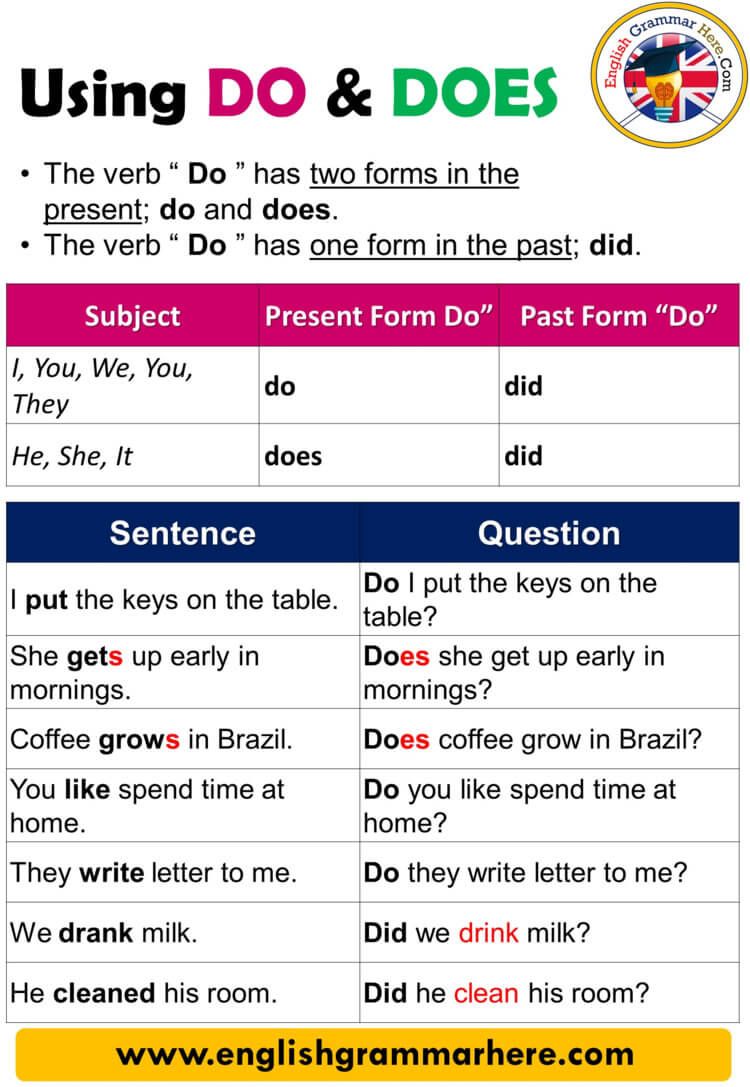
What is consideremid-careerer?
The term” mid-career” refer to a specific stage in a professional’s work life, typically occur after the early career phase but before reach senior or executive levels. Most experts define mid-career as the period between 10 and 20 years of professional experience, though this timeline can vary depend on industry, profession, and individual career trajectory.
During this stage, professionals have ordinarily develop substantial expertise in their field, establish a professional reputation, and may be considered either advancement within their current path or potential career changes.
Identify mid-career markers
Several indicators suggest you may have reached the mid career stage:
Experience level
The virtually common benchmark is had roughly 10 20 years of professional experience. This timeframe aallowsfor sufficient skill development and industry knowledge accumulation.
Professional position
Mid career professionals typically hold intermediate to senior positions but haven’t nonetheless reach executive leadership. Job titles oftentimes include words like” senior, ” ead, “” ” ” ager. ”
Salary range
Compensation ordinarily fall within the middle to upper middle salary bands for your profession and location. Mid career professionals have typically negotiated several raises or promotions beyond entry level compensation.
Responsibility level
Yourpotentiallyl have significant responsibilities, may supervise others, and make decisions that impact departmental outcomes. Nonetheless, you might not nonetheless have organization wide authority.
Age range
While age solo doesn’t determine career stage, mid career professionals are frequently between 35 and 45 years old, though this can vary wide depend on when someone enter their profession and their career progression rate.
The distinction between job and career
A common question is whether a career is but another name for a job. The answer is false – these terms represent different concepts, though they’re related.
What’s a job?
A job refer to a specific position or role with define responsibilities at a particular organization. Jobs have these characteristics:
- Specific duties and tasks
- Set working hours
- Define compensation
- Commonly short to medium term focus
- May be change oftentimes throughout life
For example,” marketing coordinator at xXYZcompany ” s a job.
What’s a career?
A career encompass the entire progression of your professional life, include multiple jobs, skill development, and advancement over time. Careers have these characteristics:
- Long term professional journey
- Series of related positions build upon each other
- Progression of skills, knowledge, and expertise
- Guide by personal and professional goals
- Oftentimes reflect professional identity
For example,” a career in marketing ” ncompass all marketing positions hold over time, along with the accumulate expertise and professional growth in that field.
Mid career challenges and opportunities
The mid-career stage present unique challenges and opportunities that distinguish it from other career phases.
Common mid-career challenges
Career plateaus
Many professionals experience a sense of stagnation during mid-career. After initial rapid advancement, progress may slow, lead to frustration or decrease motivation.
Skill relevance
Technological changes and industry evolution can make antecedent valuable skills obsolete. Mid career professionals must endlessly update their capabilities to remain competitive.
Work-life balance
This career stage oftentimes coincides with increase personal responsibilities, such as family obligations, makework-lifee balance more challenging to maintain.
Career identity questions
Mid-career can trigger reassessment of professional choices and paths, sometimes lead to the” mid career crisis ” here individuals question their career direction.
Mid-career opportunities
Leverage experience
The substantial experience accumulate by mid-career provide valuable perspective and problem solve abilities that less experienced colleagues may lack.
Professional network
By mid-career, professionals have typically build extensive professional networks that can open doors to new opportunities and collaborations.
Leadership development
This stage offer opportunities to develop and demonstrate leadership capabilities, position for senior roles.
Strategic career pivots
With established skills and experience, mid-career can be an ideal time to make strategic shifts to more fulfilling or lucrative specialties within your field.
Navigate mid-career successfully
To maximize the mid career phase, consider these strategies:
Continuous learning
Commit to ongoing professional development through formal education, certifications, or self direct learning. This help prevents skill stagnation and keep you relevant in evolve industries.
Strategic networking
Maintain and expand your professional network both within and outside your current organization. Quality connections can provide mentorship, insights, and access to opportunities not publically advertise.
Regular career assessment
Sporadically evaluate your career satisfaction, goals, and trajectory. This reflection helps identify when adjustments might be need to align your professional path with personal values and aspirations.
Mentorship roles
Consider become a mentor to early career professionals. Mentoring benefit both parties, provide fresh perspectives while reinforce your expertise and develop leadership skills.
Work life integration
Instead than strive for perfect balance, develop strategies to integrate work and personal life in sustainable ways. This might include flexible work arrangements, boundary setting, or strategic use of technology.
Mid-career transitions
The mid career stage frequently involves significant professional transitions:
Lateral moves
Sometimes career advancement mean move obliquely to gain new skills or experience in different areas before move up. These lateral moves can refresh motivation and expand capabilities.
Industry changes
Mid-career can be an optimal time to switch industries, leverage transferable skills while bring valuable outside perspective to new environments.
Entrepreneurship
Many professionals use their mid career expertise and networks to launch independent ventures, consult practices, or small businesses.
Specialization
Some choose to deepen expertise in a particular niche, becoming recognize specialists instead than pursue general management paths.
Industry variations in mid-career definition
The definition of mid-career varies importantly across different fields:

Source: beaconfinancialstrategies.com
Technology
In speedily evolve tech fields, mid career might begin after but 5 7 years due to the accelerated pace of change and skill development.
Medicine
Medical professionals oftentimes have extended training periods, witmid-careerer potentially start 15 20 years after begin medical school.
Academia
Academic mid-career typically align with achieve tenure and associate professorship, ordinarily 7 10 years after complete a doctorate.
Trades
In skilled trades, mid-career oftentimes begin after complete apprenticeship and gain several years of journeyman experience.
The future of mid-career in change work environments
Several trends are reshaped what mid career means:

Source: ktscareercoaching.com
Extended working lives
As people work yearn before retirement, the mid-career phase may expand, potentially last 20 + years sooner than the traditional 10 15.
Multiple careers
Progressively, professionals pursue several distinct careers throughout their work lives, create multiple mid-career phases in different fields.
Remote work implications
Distribute workforces change advancement patterns, potentially create new mid-career paths base on virtual leadership and global collaboration skills.
Skill base advancement
Traditional time base career progression is give way to skill base advancement, mean mid-career status may be determined more by capability than years of experience.
Conclusion
The mid career stage represents a critical period of professional development characterize by substantial experience, establish expertise, and important career decisions. While a job refer to a specific position, a careerencompassess your entire professional journey across multiple positions and organizations.
Understand the distinction between these terms and recognize the unique characteristics of the mid career phase can help professionals navigate this period more efficaciously. By embrace continuous learning, strategic networking, and periodic self assessment, mid career professionals can overcome common challenges and leverage their experience for continued growth and satisfaction.
Whether you’re look to advance in your current path, pivot to new opportunities, or achieve better work life integration, the mid-career stage offer valuable perspective and capabilities that can be strategically deploy to achieve your professional goals.